Read article 'Super-massive black holes quickly repoint their jets'
Read article 'Super-massive black holes quickly repoint their jets'
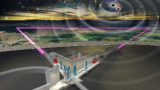
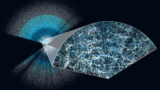
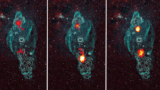
Super-massive black holes quickly repoint their jets
Francesco Ubertosi of the University of Bologna and co-workers studied a sample of about 60 clusters observed using the Very Long Baseline Array and the Chandra X-ray telescope.